Demystifying Optical Character Recognition (OCR) in Accounts Receivable
- 14 min read
Optical character recognition is the process that converts an image of text into a machine-readable text format. It eliminates the need for humans to manually interpret and transfer information from a physical document to a digital medium.
In this article, we explore what OCR is and its impact on finance—broadly—and accounts receivable—more specifically.
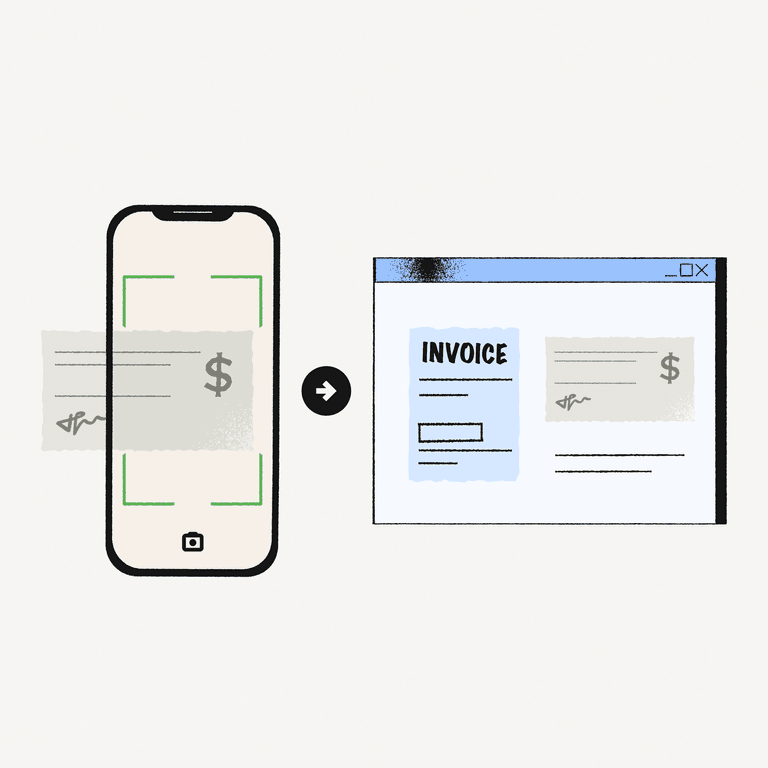
No one likes entering data manually. It’s time-consuming, expensive, and prone to errors. Yet, many businesses still find themselves overwhelmed with physical documents that require manual entry. This is especially true for business functions like accounts receivable (AR), where paper checks, invoices, and remittance data are still quite common.
Thanks to optical character recognition (OCR), that could soon be a problem of the past. This technology allows for information from a physical document to be digitized into editable and usable data, without requiring a human to key it in by hand. It presents a major breakthrough in how data entry—and more complex activities, like cash application—is performed.
In this article, we’ll tell you what optical character recognition is, how it works, and how you can apply this technology to your accounts receivable team’s daily tasks.
Jump to a section of interest:
- What optical character recognition (OCR) is
- The 4 different types of optical character recognition
- How optical character recognition works
- The benefits of optical character recognition
- How optical character recognition applies to finance
- How optical character recognition benefits accounts receivable
What is optical character recognition (OCR)?
Optical character recognition is defined as “the process that converts an image of text into a machine-readable text format.” Its main purpose is to eliminate the need for a human to manually interpret and transfer information from a physical document to a digital medium.
Though it may seem complicated, there’s a good chance it’s already made your life easier. If you’ve ever taken a picture of a receipt and uploaded it to an expense portal, there’s a very good chance that process was powered by OCR.
What are the different types of optical character recognition?
Currently, there are four widely recognized types of OCR:
- Simple optical character recognition software
- Intelligent character recognition software (ICR)
- Intelligent word recognition
- Optical mark recognition
Each possesses its own unique abilities, and can be used to solve specific problems or use cases.
1. Simple optical character recognition software
As indicated by the name, this is the most basic type of OCR. With simple optical character recognition software, an OCR engine stores a significant number of font and text image patterns that it uses as templates.
Using pattern-matching algorithms, the software compares the image containing text to those templates character-by-character. From there, it finds matches and recreates them digitally. Because there are so many different fonts and styles of writing, not every possibility can be contained in the database. This is the largest limitation on this type of OCR.
2. Intelligent character recognition software
This type of optical character recognition goes beyond simply matching characters to a static, predetermined database of characters. Rather, it uses machine learning and artificial intelligence to interpret different styles of fonts and handwriting.
Much like a human, this type of OCR can analyze all the elements that make up letters and numbers, such as curves, lines, and spaces.
3. Intelligent word recognition
Intelligent word recognition uses essentially the same underlying technology and processes as ICR. However, as the name dictates, this optical character recognition variant reads entire words, rather than just individual characters.
Because of this, intelligent word recognition is generally considered the go-to OCR method for digitizing freehand writing.
4. Optical mark recognition
Unlike the other three types of OCR, optical mark recognition does not digitize physical documents. Rather than searching for words or numbers, this method of optical character recognition looks for items like logos and watermarks in images. Its use case is much more specific, with a focus on finding inappropriately used logos or unlicensed images.
—
Curious about how real businesses have benefited from OCR? This on-demand webinar highlights how this technology helped a Versapay client grow their business without adding staff.
How optical character recognition works
Getting results from OCR isn’t as easy as just snapping a quick picture. To successfully digitize documents, optical character recognition follows four steps:
- Image acquisition
- Preprocessing
- Text recognition
- Post-processing
Step 1: Image acquisition
The first requirement is to capture an image of the physical document you want to digitize. This is often done using a camera, which reads the image and converts it into binary data that software can understand. To accomplish this, the optical character recognition software separates the dark portion of the document (text) from the light portion (background).
Step 2: Preprocessing
Before the data can be read, the optical character recognition software first needs to clean up the captured document to remove extraneous elements that could negatively affect accuracy. This tidying process includes ensuring documents are properly aligned, lines and boxes are unblemished, and digital spots removed.
Step 3: Text recognition
Now that the text has been captured and cleaned, it’s time to transform it into its digital output. This is done in two different ways: pattern-matching and feature extraction.
- Pattern matching—This method attempts to match each individual character with a similar character stored in the OCR software’s engine. It only works if there is a comparable character stored. As such, this method is best for translating fonts that were originally generated in a standardized font, such as from a computer rather than handwriting.
- Feature extraction—Rather than trying to match the character as a whole, this optical character recognition method looks at the content as individual loops, lines, directions, and intersections. It then attempts to match those features to pre-stored glyphs.
Step 4: Post-processing
Once the software has processed the data, it’s then outputted into the digital format you’ve selected. This is often a spreadsheet or PDF.
What are the benefits of optical character recognition?
The benefits of optical character recognition are wide-ranging, and vary largely based on how you’re applying the technology. Across all use cases, these are generally the top four:
- Accelerated processes
- Reduced costs
- Increased accuracy
- Improved searchability
1. OCR accelerates data entry processes
Imagine you’re a finance clerk tasked with entering invoices your company receives into your ERP system. If you’re dealing with a significant number of invoices, or invoices with many details, this process would quickly become overwhelming. As a result of the heavy workload, your work begins to slow and you start to make more errors.
Optical character recognition can digitize these invoices significantly faster than a human. For businesses, that means spending significantly less time waiting for what may be critical documents to become accessible online.
2. OCR reduces data entry costs
Having humans digitize physical documents isn’t just slow—it’s also expensive. Each person you hire to perform data entry eats into your bottom line. Optical character recognition can eliminate these expenses, and allow you to redirect your resources to work that is both more fulfilling and more valuable.
3. OCR increases data input accuracy
Because the clarity of data ranges so widely, it’s difficult to identify an exact level of average accuracy for optical character recognition. However, some experts consider an accuracy rate of 90% to 98% to be the benchmark.
Regardless, this is a rate most humans would have a very difficult time keeping up with. That’s especially true considering humans tend to make more mistakes as they work longer and grow tired, whereas software does not.
4. OCR improves document searchability
If you had a printed document such as an invoice, and needed to find a specific piece of information like a payment amount or date, you’d have to flip through pages and pages to hopefully find what you’re looking for. By digitizing that document using optical character recognition, finding something is often as easy as opening the program’s search bar and typing in the words you’re looking for. That means faster answers, and less time wasted.
How optical character recognition applies to finance
Finance is an area where OCR has especially high potential for performance. This is because the physical documents it tends to analyze, such as receipts, invoices, or spreadsheets, are typically highly structured.
In other fields, such as creative production, where processing a handwritten script might be a more common request, the data is much less structured, meaning it will take longer for OCR to process, and may do so with more errors.
Throughout the broader field of finance, optical character recognition offers 3 main benefits:
- Simplified expense management
- Streamlined accounts payable
- Enhanced mobile finance capabilities
1. Optical character recognition simplifies expense management
Though it would be nice if all employees could be trusted 100% of the time, there are some who attempt to take advantage of the company by submitting blank or false expense reports.
By requiring expenses to be uploaded through an OCR software, it’s much more difficult for a reimbursable amount to be faked. And when it’s time for expenses to be audited, the simplified searchability provided by digitization makes doing this much less time consuming.
2. Optical character recognition streamlines accounts payable
For businesses that receive a high volume of invoices, a significant amount of manual work is often required to upload them to internal systems—like accounts payable portals. Not only is it labor intensive, but this process also leads to manual errors. OCR accelerates this process and ensures accuracy by capturing and processing invoices in a fraction of the time with a fraction of the errors.
3. Optical character recognition enhances mobile finance capabilities
Though perhaps a lesser benefit, OCR allows you to do more on mobile devices. For example, finance teams can have employees submit receipts while they’re on the go, allowing for faster repayment.
Similarly, banks can allow their customers to deposit checks through mobile apps by capturing images of the check using optical character recognition. This saves their customers time, and makes them less reliant on costlier options like depositing checks in person at a bank branch.
How is optical character recognition used in accounts receivable?
Within finance, accounts receivable stands out as a function where OCR is especially useful. This is because even with the rise of digital payments—like eChecks—many companies still rely on physical documents like checks, invoices, and remittance advice.
Currently, OCR in accounts receivable has two main uses:
- Check processing, and
- Cash application.
At Versapay, we apply them both to our solutions.
1. Check processing using optical character recognition
Before OCR, a person was required to input checks. This meant a human was processing and verifying each check one-by-one, delaying how quickly you could complete a payment and receive your funds.
With OCR, an image of a check is captured and digitized for deposit. This allows it to be processed considerably faster than a human. As a result, the recipient of the check is able to access those funds much faster, a critical aspect of healthy cash flow. Plus, with the check digitized, the next step in the process, cash application, can be greatly simplified.
2. Cash application using optical character recognition
This process traditionally involves matching payments on invoices to outstanding receivables by having a human search for and compare documents. However, with documents in so many formats and locations, this is not only a slow process, but also prone to errors.
With OCR, almost all of those documents can be captured quickly and made available in one central location. This dramatically improves efficiency and completes the cash application faster, helping to accelerate cash flow.
And when optical character recognition is part of an AI-powered cash application solution like Versapay’s, the benefits are even greater. These solutions are able to look across all pertinent documents nearly instantaneously and make informed decisions about how a payment can be applied. For example, they can:
- Interpret unclear or missing information to apply a payment
- Match one payment to multiple invoices—automatically, without human intervention—by finding the sum of invoices that match the payment
Plus, thanks to machine learning, the solution becomes more accurate each time it’s used, allowing for over 90% straight-through processing.
Put optical character recognition to work for your organization
As you can see, optical character recognition software is extremely powerful with a variety of applications—especially in accounts receivable, and more specifically, the cash application field. Employed correctly, it can help you significantly reduce your costs, while also completing important tasks more quickly and with greater accuracy.
If you’re looking for somewhere to start, cash application is the perfect opportunity—and our AI-powered cash application solution offers exactly that. Check it out to learn how it can help your accounts receivable team accomplish significantly more with much less work.
About the author

Joe Crawford
Joe Crawford is the Senior Copywriter at Versapay. While currently focused on Fintech, he’s written extensively across industries including automotive, telecom, and communications technology. Coming from a background in comedy, he welcomes any chance he can to introduce some levity to world of Accounts Receivable.


